What is Xetra?
Xetra is an electronic trading platform operated by the Frankfurt Stock Exchange (FWB). The platform was launched in 1997 and can be used to trade shares, bonds, funds, warrantsand commodity contracts electronically. Xetra was one of the first global electronic trading systems and still lists the DAX 30 index. The DAX 30 is the German benchmark index for the stock market. More than 90% of share trading on all German stock exchanges is conducted via Xetra. This makes Xetra the largest of the seven German stock exchanges. In addition, around 30% of all trading inexchange-traded funds (ETFs) in continental Europe is conducted via Xetra. In the DAX stocks, Xetra even has a market share of over 60% across Europe.
The Xetra trading model
Pricing on Xetra is based on clearly defined rules. Market orders and limit orders are permitted in the trading forms for the pricing process. However, the order types can be further specified. In addition, the Xetra trading platform uses the “continuous trading with auctions” trading model. This is a combination of the “Auction”, “Continuous Trading” and “Trade-at-Close” trading models. Continuous trading means that buy and sell orders are executed immediately at the current market price. Liquidity is bundled on the trading venue by offering three additional auctions per day. In addition, trade-at-close allows market participants to continue trading after the closing auction at the official closing price of the auction for a limited period (maximum 10 minutes).
The following chart shows the Xetra auction schedule.
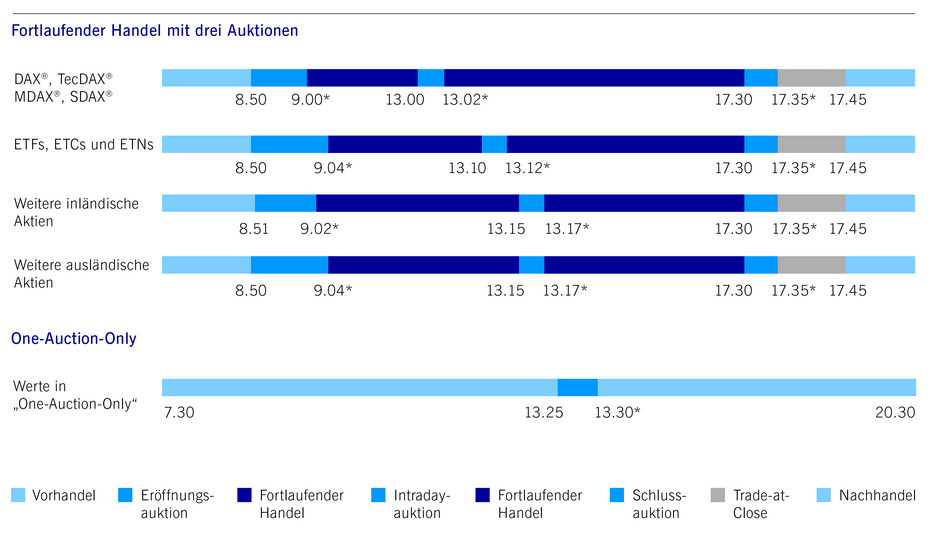
Source: www.xetra.com
*Auctions have a random end. The times given are the earliest time at which an auction ends.
Other electronic trading systems
In the USA, Instinet (originally Institutional Networks) was introduced in 1969 as the first automated system for direct trading between American institutions. Nasdaq was the second automated system, introduced in 1971. Shortly afterwards, the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) introduced its DOT (Designated Order Turnaround) system. In 1984, SuperDOT was launched, which increased the number of shares traded simultaneously to almost 100,000. Nasdaq soon offered the Small Order Execution System (SOES) to compete with the NYSE.
The first fully electronic exchange in Germany was the Deutsche Terminbörse (DTB), which was introduced in 1990. Today, in addition to Xetra, there are also Xontro and Tradegate for the cash market and Eurex for the derivatives market. Trayport is a platform on which energy and commodity trading takes place in Europe. Not only stock exchanges, but also large financial brokers operate trading platforms.

