What is a securities portfolio?
A securities portfolio is a compilation of securities. Securities are various financial products, such as shares, bonds (fixed-interest securities), fund units and structured products. The possible range of assets that can be added to a securities portfolio is broad. Another example is real estate. A securities portfolio can generally be managed in-house. In many cases, it is worth commissioning a good, independent asset manager to manage the securities portfolio, as the optimal allocation can be very complex.
Portfolio management
A key advantage of the securities portfolio is that the risk can be reduced through diversification. The risk is spread, for example , by selecting different securities from different sectors . Different sectors are usually exposed to different risks. For example, not all sectors are equally affected by the coronavirus crisis. Food retailers, online retailers and delivery services, logistics companies and parcel services, the pharmaceutical industry and medical technology, for example, have benefited from the pandemic. Securities from this sector have increased in value, while securities from the aviation, tourism and event industries, for example, have lost value. A balanced securities portfolio can use the gains from the currently strong sectors to offset the losses from the currently weak sectors. The aim of diversification is therefore to reduce the risk of individual securities or individual financial products while keeping returns as constant as possible, or to maximize returns while maintaining the same level of risk. This is achieved by investing in different areas, each of which would react differently to the same event. There are many ways to diversify, such as diversification in different asset classes (equities, real estate, gold, bonds, etc.), in different regions and countries, or diversification over time (staggered purchases/sales of securities). Regardless of the composition, all portfolios should have a certain degree of diversification and reflect the risk tolerance, return targets, time horizon and other relevant aspects, such as tax conditions, liquidity requirements, legal situation and other special circumstances.
The investor’s risk profile and types of securities portfolio
There are many different types of securities portfolios. A hybrid securities portfolio, for example, is diversified across different asset classes. A portfolio investment can either be strategic, i.e. financial investments are bought with the intention of holding them for the long term, or tactical, i.e. investments are actively bought and sold in the hope of achieving short-term gains.
Figuratively, a securities portfolio can be thought of as a cake made up of different sized pieces. Each piece represents a different asset class. Depending on the investor’s risk tolerance, a wide variety of securities portfolios can be put together. Below are 3 examples of portfolios according to risk type.
Examples
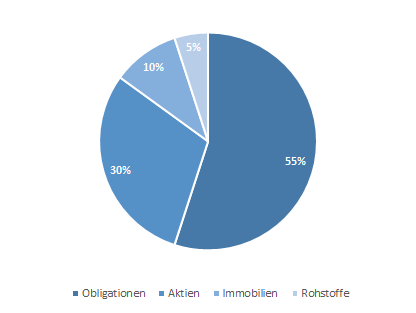
Safety-oriented
Portfolio
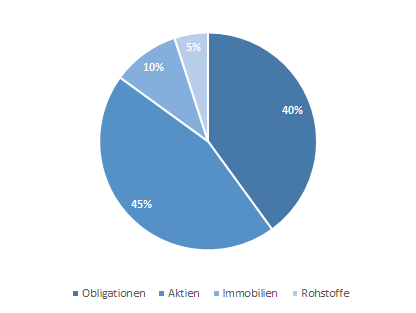
Balanced
Portfolio
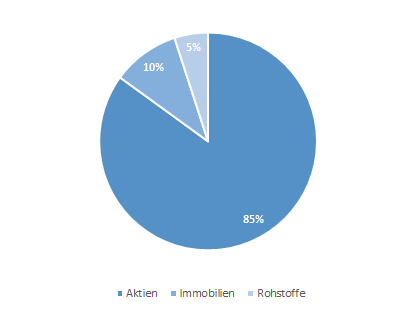
Growth-oriented
Portfolio
An investor who does not want to take on a lot of fluctuation risk could, for example, invest in a portfolio with a high proportion of fixed-income securities and a smaller proportion of equities, real estate and commodities. The risk/return profile is therefore low. This example is illustrated by the security-oriented portfolio. It is also possible to increase the proportion of equities despite a low risk tolerance, for example by choosing a defensive, equity-oriented securities portfolio. Consumer staples shares can be selected for this purpose. These generally have a low risk, as they are less susceptible to crises than other sectors. These shares often exhibit lower price fluctuations in both good and bad times.
A balanced investor, on the other hand, could increase the proportion of equities (or real estate and commodities) somewhat. This increases the fluctuation risk and therefore also the potential return. This is illustrated by the balanced portfolio.
A growth-oriented investor is prepared to take fluctuation risks for higher returns. The growth-oriented portfolio is exposed to greater fluctuations in value due to the high proportion of equities. This has a positive effect on the potential return. However, the fluctuations in value can be both positive (gains) and negative (losses).
As a rule, yield and equity-oriented securities portfolios have a higher fluctuation risk in order to achieve high returns. However, value fluctuations in portfolios can also have other causes. For example, yield-oriented investors may look for companies that are in an early growth phase or stocks that are rumored to be takeover targets. Technology or healthcare companies that are in the process of developing a breakthrough product also fall into this category.
The time horizon and the securities portfolio
allocation
Similar to risk tolerance, investors should consider how long they want to, or can, invest when constructing a portfolio. In general, investors should favor a conservative asset allocation the shorter their investment horizon in order to protect the portfolio’s returns until that time.

